Relief and Structure of Telangana
Introduction:
Telangana, also spelled Telengana or Telingana, constituent state of south-central India. It is bordered by the states of Maharashtra to the north, Chhattisgarh and Odisha to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the southeast and south, and Karnataka to the west. The area of what is now Telangana constituted the north-central and northeastern portions of Andhra Pradesh for almost six decades, but on June 2, 2014, that territory was calved off to form a separate state. The capital of both Telangana and Andhra
Pradesh is Hyderabad, in west-central Telangana.TelenganaPlateau :
Telengana Plateau, Telengana also spelled Telangana, plateau in western Andhra Pradesh state, southeastern India. Comprising the northeastern part of the Deccan plateau, the Telengana Plateau has an area of about 57,370 square miles (148,000 square km), a north-south length of about 480 miles (770 km), and an east-west width of about 320 miles (515 km). Mentioned in one of the Mauryan emperor Ashoka’s edicts, the region was successively ruled by the Satavahanas,
The plateau is drained by the Godavari River taking a southeasterly course; by the Krishna River, which divides the peneplain into two regions; and by the Penneru River flowing in a northerly direction. The plateau’s forests are moist deciduous, dry deciduous, and tropical thorn.
Features of Telangana: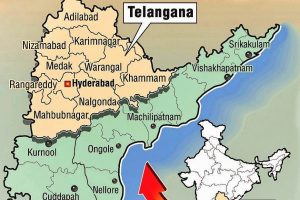
Telangana is situated on the Deccan Platue in the Indian Peninsula. The region is drained by two major rivers Godavari and River Krishna, but most of the land is arid. Telangana is also drained by several minor rivers such as the bhima, the maner, the manjira and the musi.
The annual rainfall is between 900 and 1500 mm in northern Telangana and 700 to 900 mm in southern Telangana, from the southwest monsoons. Various soil types abound, including chalkas, red sandy soils, dubbas, deep red loamy soils, and very deep black cotton soils that facilitate planting mangoes, oranges and flowers.
Geography of Telangana:
Telangana has an area of 1,14,800 square kilometres and it is drained by two major rivers, Krishna and Godavari. The river Godavari flows on the north, whereas Krishna flows in the south. Apart from these rivers, there are other small rivers such as Bhima, Dindi, Manjeera, Manair, Kinnerasani, Moosietc, which also flow through Telangana. 45% of the forest area of Andhra Pradesh is in the state of Telangana. It also has a vast coal deposit and around 20% of India’s coal deposit lies in Telangana. The coal produced from this region is supplied to the states in south India.
Telangana lies between 15°46’and 19°47′ N latitude and 77° 16′ and 81° 43’E longitude, and is bordered by the states of Maharashtra in the north and north-west, Karnataka in the west, Chhattisgarh in the north-east and AndhraPradesh in the south and east. The average annual rainfall is about 906 mm, 80% of which is received from the Southwest monsoon. The State is strategically located in the Deccan Plateau in a semi-arid zone. The climate is predominately hot and dry.
Relief and Structure of Telangana:
The relief features of a region in Geography means the high altitude areas, mountains, peaks, valleys, low lying areas etc. These relief features divide the main lands into living areas, forests, islands, waste lands, river plains etc.
The telangana is on the Deccan plateau. It is on the central stretch of the Eastern seaboard of the Indian Peninsula. Major Rivers Godavari and Krishna flow through the state. The state is divided into two main regions. There are ghats and peneplains. There are many low depressions in the land. There are thick forest regions in the state. There are some Eastern ghats that border the state.
There are many small local reliefs in Telangana of height about 300 m, small summit areas and having steep slopes. There are not any notable valleys in the region. The altitudes of lands (hill tops) in the state range from 500 m to 800 m.
It is situated on the Deccan plateau, Telangana state occupies 1.14 lakh sq km on the central stretch of the eastern seaboard of the Indian peninsula.
Despite the region drained by two major rivers – 69% of Krishna’s catchment areas and 79% of Godavari – most of the land is dry and arid. There are also minor rivers like Bhima, Manjira and Musi that crisscross the state comprising 10 districts in all.
The annual rainfall ranges from 900 to 1,500 mm in northern Telangana and 700 to 900 mm in southern Telangana, mostly getting the precipitation from the southwest monsoon.
Various soil types are found in Telangana – chalkas, red sandy soils, dubbas, deep red loamy soils, and very deep b.c.soils – that facilitate planting mangoes, oranges and flowers.
It is noteworthy that 45% of forest cover of undivided Andhra is now located in the five districts of Telangana.
Much of its area is occupied by the Telangana plateau in the north and the Golconda plateau in the south and is composed of gneissic rock.
The plateau’s average elevation is about 1,600 feet with its peaks in the west
and southwest and gradually sloping down towards the east and northeast, where it meets the disjointed ridges of
the Eastern Ghats ranges.Climate in Telangana
The summer begins from March to end in June, followed by a period of tropical rains from July to September; and finally, winter occurs from October to February.
Summers are very warm to extreme hot and dry, with temperatures often crossing 42-43 degree Celsius.
The annual precipitation mostly from the rainy southwest monsoon winds varies across the state. It averages about 35 inches (900 mm) per year, although the annual total often varies considerably from the average and can be as little as 20 inches (500 mm) in drier areas.
The average minimum temperatures in Hyderabad reach about 15 degree Celsius in January and February, while in the elevated areas it falls between 10 and 12 degree Celsius in the winter.
TSPSC Notes brings Prelims and Mains programs for TSPSC Prelims and TSPSC Mains Exam preparation. Various Programs initiated by TSPSC Notes are as follows:-
- TSPSC Mains Tests and Notes Program
- TSPSC Group I Prelims Exam 2024- Test Series and Notes Program
- TSPSC Prelims and Mains Tests Series and Notes Program
- TSPSC Detailed Complete Prelims Notes